Current Air Quality Conditions: Real-Time PM2.5 and AQI Levels
are essential information for anyone concerned about their health and the environment. PM2.5, or fine particulate matter, is a major air pollutant that can cause a variety of health problems, including respiratory and cardiovascular disease. AQI, or Air Quality Index, is a measure of the level of air pollution in a given area.
Editor's Notes: Current Air Quality Conditions: Real-Time PM2.5 and AQI Levels published today.
This topic is important because it can help you make informed decisions about your health and safety.
To help you understand this complex topic, below you will find a detailed guide to Current Air Quality Conditions: Real-Time PM2.5 and AQI Levels
Key differences or key takeaways:
| PM2.5 | AQI |
|---|---|
| Fine particulate matter | Air Quality Index |
| Measured in micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m3) | Measured on a scale of 0 to 500 |
| Can cause a variety of health problems, including respiratory and cardiovascular disease | Provides information about the level of air pollution in a given area |
FAQ
This section provides comprehensive answers to frequently asked questions regarding current air quality conditions, real-time PM2.5 levels, and AQI readings.
Question 1: What is PM2.5 and why is it important to monitor?
PM2.5 refers to particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less. These microscopic particles can penetrate deeply into the lungs and pose significant health risks, including respiratory and cardiovascular issues. Accurate monitoring of PM2.5 levels is crucial to assess potential health impacts and mitigate exposure.
Question 2: How does the Air Quality Index (AQI) work?
The AQI is a standardized measure that categorizes air quality levels based on various air pollutants, including PM2.5. Each pollutant has specific concentration ranges corresponding to different AQI levels, ranging from 'Good' to 'Hazardous'. The AQI provides a comprehensive assessment of overall air quality and its potential health implications.
Question 3: What are the major sources of PM2.5?
PM2.5 emissions primarily come from combustion processes, both natural and human-induced. Natural sources include wildfires, forest fires, and volcanic eruptions. Human activities such as burning fossil fuels in vehicles, industrial processes, and certain agricultural practices also contribute significantly to PM2.5 emissions.
Question 4: How can I protect myself from PM2.5 exposure?
Limiting exposure to PM2.5 is crucial for health protection. Avoid prolonged outdoor activities during periods of high PM2.5 levels. If exposure is unavoidable, consider using face masks or respirators specifically designed to filter PM2.5 particles. Additionally, supporting policies that aim to reduce PM2.5 emissions is essential for long-term community health.
Question 5: What are the long-term health effects of PM2.5 exposure?
Chronic exposure to PM2.5 can lead to severe health complications, including increased risk of cardiovascular disease, respiratory illnesses, stroke, and even premature death. Prolonged exposure can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to other infections and diseases.
Question 6: How can I stay informed about current air quality conditions?
Real-time air quality monitoring systems provide up-to-date information on PM2.5 levels and AQI readings. Check official government websites, environmental agencies, or mobile applications for accurate and timely air quality data. Staying informed empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding outdoor activities and exposure.
Monitoring current air quality conditions, understanding the health implications of PM2.5 exposure, and taking appropriate protective measures are essential for maintaining health and well-being in the face of air pollution.
Transition to the next article section:
Tips
To stay updated on the current air quality conditions and protect your health from the harmful effects of air pollution, follow these tips:
Tip 1: Check real-time air quality conditions Current Air Quality Conditions: Real-Time PM2.5 And AQI Levels.
Knowing the air quality in your area will help you make informed decisions about when to limit outdoor activities or take precautions while outside.
Tip 2: Consider using an air purifier.
Air purifiers can help reduce indoor air pollution by removing harmful particles such as PM2.5 and allergens.
Tip 3: Avoid outdoor activities when air pollution is high.
When air quality is poor, it's best to limit time spent outdoors, especially for sensitive individuals, children, and the elderly.
Tip 4: Close windows and doors on polluted days.
Keeping windows and doors closed will help prevent outdoor air pollution from infiltrating your home.
Tip 5: Wear a face mask outdoors when air pollution is high.
Wearing a face mask outdoors can help reduce exposure to harmful air pollutants.
Tip 6: Take public transportation or carpool.
Reducing the number of vehicles on the road can help improve air quality.
Tip 7: Support clean energy initiatives.
Investing in renewable energy sources and reducing energy consumption can help reduce air pollution.
Tip 8: Plant trees.
Trees can help improve air quality by absorbing air pollutants.
By following these tips, you can help improve your health and well-being by reducing your exposure to air pollution.
Current Air Quality Conditions: Real-Time PM2.5 And AQI Levels
Understanding real-time PM2.5 and AQI levels is crucial for assessing air quality conditions and devising effective strategies for improving them. These key aspects help us interpret and act on air quality data:
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5): Fine particulate matter, less than 2.5 micrometers in size.
- Air Quality Index (AQI): A standardized measure of air pollution levels, with various categories indicating health risks.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous measurement of air quality, providing up-to-date information.
- Health Impacts: PM2.5 and AQI levels can significantly affect human health, causing respiratory and cardiovascular issues.
- Emission Sources: Identifying sources of air pollution, such as vehicles, industrial activities, and biomass burning, is crucial for mitigation.
- Air Quality Forecasting: Predicting future air quality conditions based on historical data and weather patterns helps plan for potential health risks.
Monitoring real-time PM2.5 and AQI levels empowers us to make informed decisions about our daily activities, such as limiting outdoor exposure during high pollution days. Continuous monitoring also helps governments and environmental agencies regulate air pollution sources and implement effective policies to improve air quality. By understanding and addressing these key aspects, we can collectively work towards cleaner, healthier air for all.
Chart_US.png)
What is the air quality index (AQI)? | IQAir - Source www.iqair.com
Current Air Quality Conditions: Real-Time PM2.5 And AQI Levels
Current air quality conditions are heavily influenced by the levels of PM2.5 and AQI. PM2.5 refers to particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less, while AQI stands for Air Quality Index. These factors provide a comprehensive understanding of the air quality in a particular area. PM2.5 is a major pollutant that can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and even cancer. AQI, on the other hand, is a measure of the overall air quality and is based on the concentration of various pollutants in the air, including PM2.5.
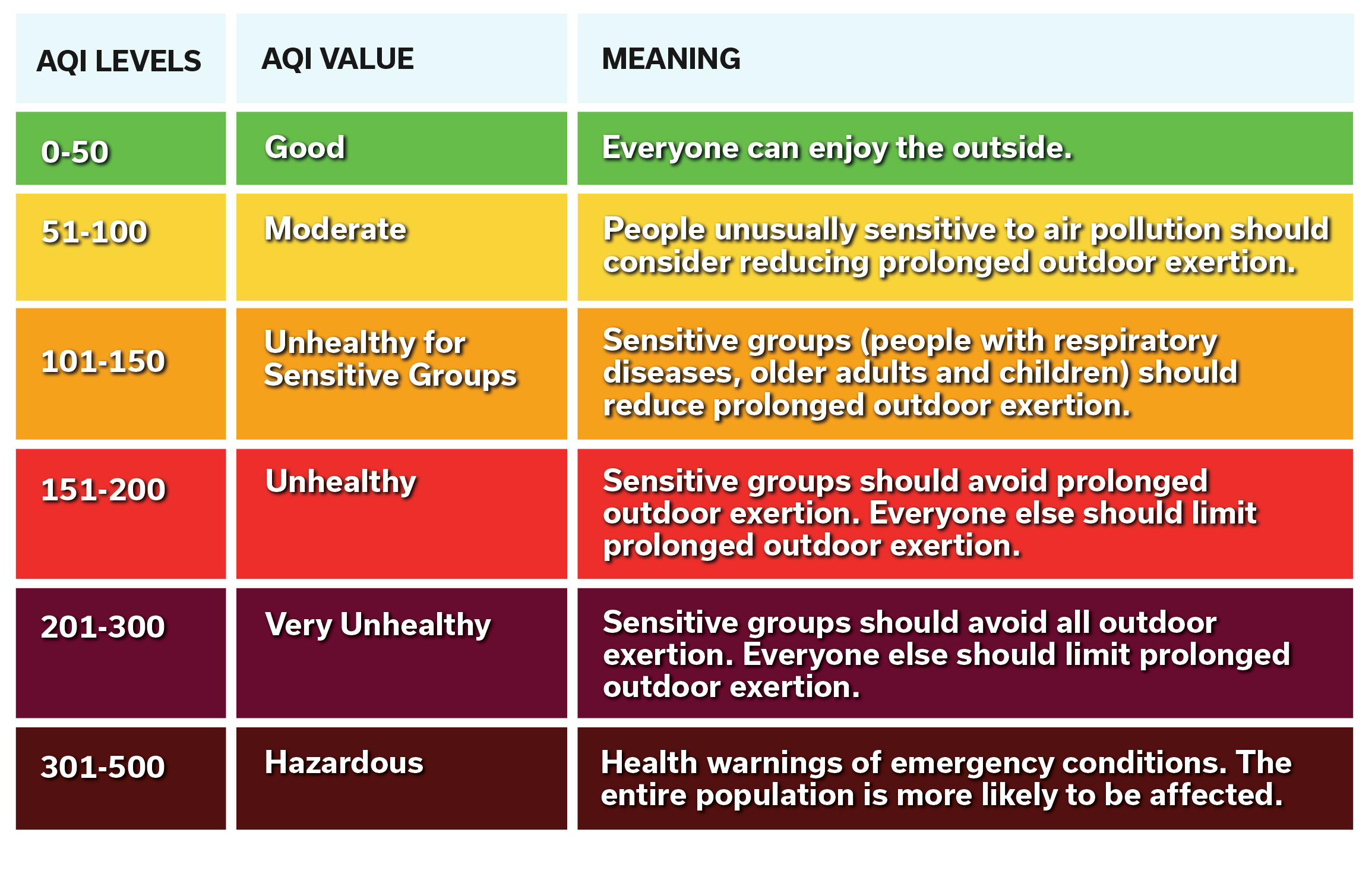
AIR QUALITY INDEX | Clean Air Michiana - Source www.cleanairmichiana.com
Monitoring PM2.5 and AQI levels in real-time is essential for public health. It helps individuals make informed decisions about their activities and exposure to outdoor air pollution. High levels of PM2.5 and AQI can indicate unhealthy air quality, which can be harmful to sensitive groups such as children, the elderly, and those with respiratory conditions. Real-time data on these parameters allows for timely warnings and preventive measures to be implemented.
Moreover, understanding the connection between PM2.5 and AQI levels is crucial for effective air quality management. By identifying sources of PM2.5 emissions and implementing targeted control measures, policymakers can improve air quality and protect public health. This can involve reducing emissions from vehicles, industries, and construction activities, as well as promoting cleaner energy sources and sustainable transportation.
In conclusion, real-time monitoring of PM2.5 and AQI levels provides valuable information for assessing air quality and safeguarding public health. The connection between these parameters highlights the importance of addressing PM2.5 emissions and implementing comprehensive air quality management strategies to create healthier and more sustainable environments.
Table: PM2.5 and AQI Levels
| PM2.5 Level (μg/m³) | AQI Category | Health Effects |
|---|---|---|
| 0-12 | Good | Minimal health risks |
| 12.1-35.4 | Moderate | May cause mild respiratory symptoms in sensitive groups |
| 35.5-55.4 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups | May cause respiratory and cardiovascular symptoms in sensitive groups |
| 55.5-150.4 | Unhealthy | May cause respiratory and cardiovascular symptoms in the general population |
| 150.5-250.4 | Very unhealthy | May cause serious respiratory and cardiovascular symptoms |
| 250.5+ | Hazardous | May cause severe respiratory and cardiovascular symptoms, even in healthy individuals |